Research on Climate Change Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for Domestic Electrical Grids
Background:
Climate change poses significant challenges to the energy sector, particularly in developing nations where electrical grids are major sources of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. To address these challenges, this study introduces an Integrated Quantification Approach (IQA) tailored for developing countries, emphasizing renewable energy integration, demand-side management (DSM), and energy-efficient devices (EEDs). By evaluating the impacts of ambient temperature increases (0.5 °C to 2 °C) on thermal power generation and transformers, this framework provides actionable insights into reducing emissions and improving grid efficiency.
Quantitative Framework:
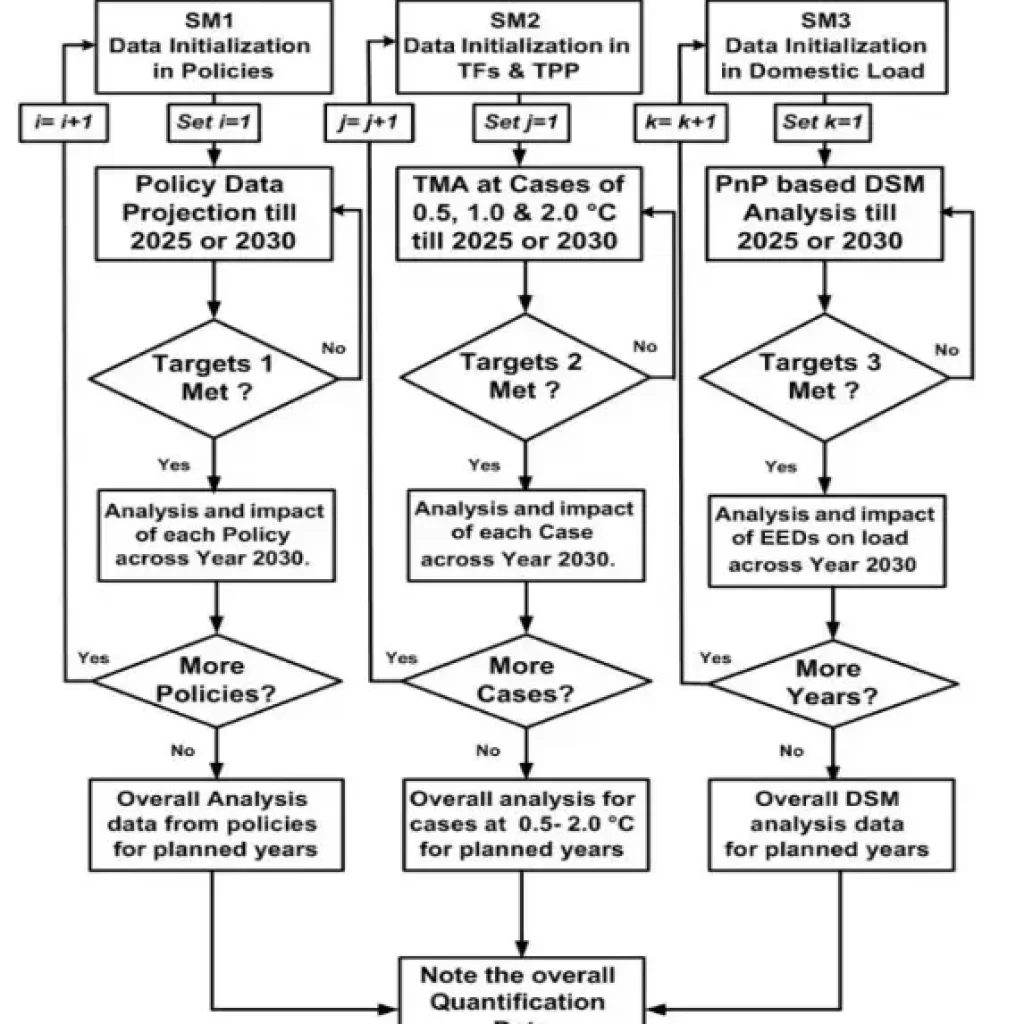
The IQA incorporates historical data extrapolation, real-time analysis, and thermal modeling (TMA) to project future GHG reduction and renewable energy trends. It integrates EEDs into domestic load profiles through plug-and-play algorithms, optimizing energy consumption while enhancing user comfort. Comparative analyses of policies for developed and developing nations highlight the significant potential for emissions curtailment in Pakistan.
Results and Impacts:
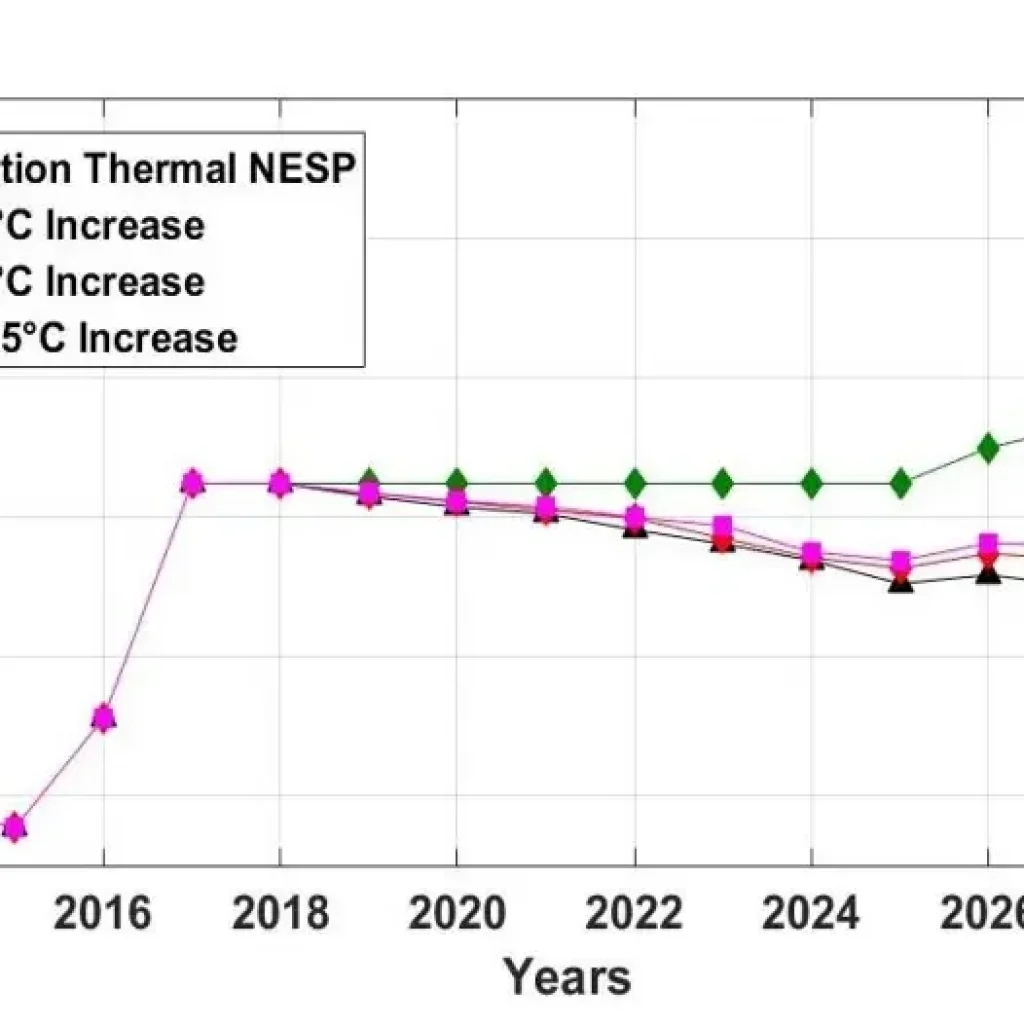
The share of thermal energy in the mix decreases from 68.43% to 40.2% by 2030, with CO2 emissions dropping by 55% compared to the base case.
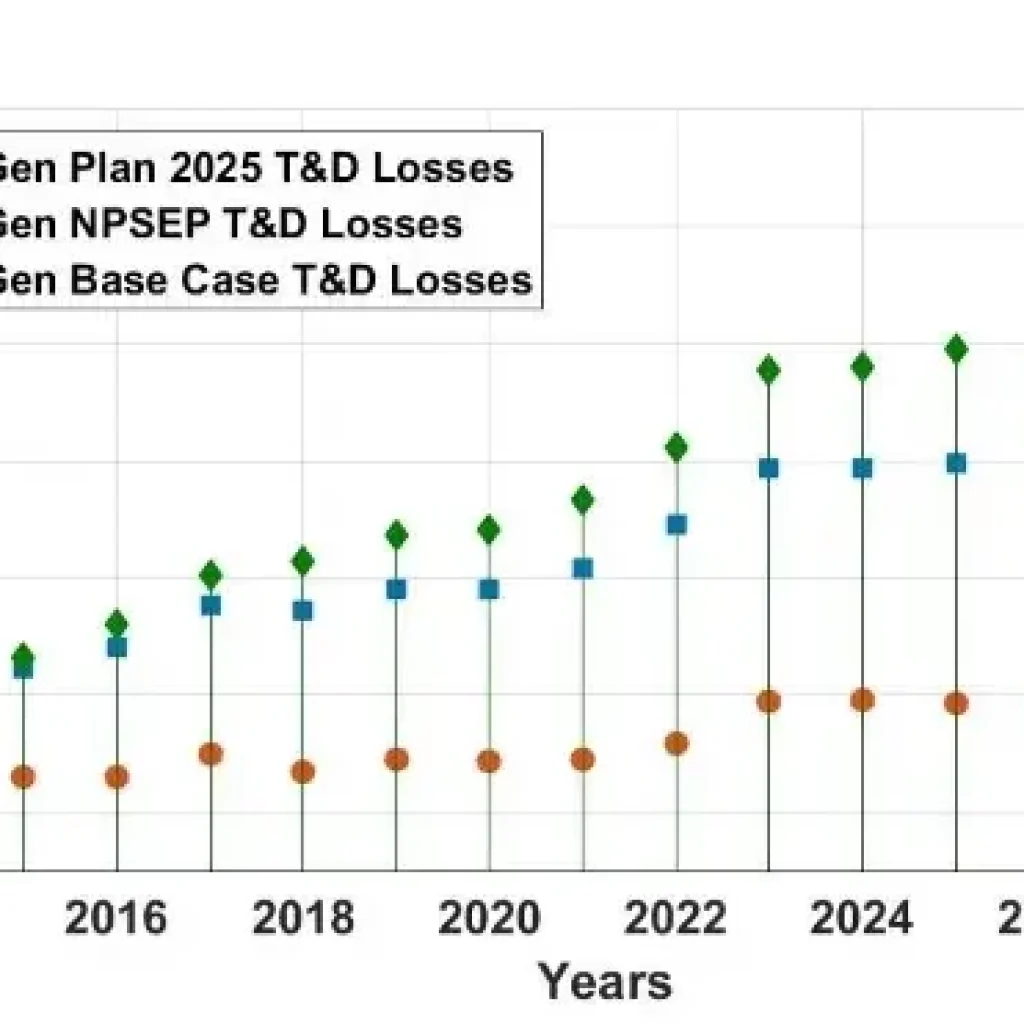
Transmission and generation losses due to climate impacts are quantified, with transformer losses rising from 180 MW to 1770 MW and thermal plant losses reaching 1440 MW by 2030.
EED adoption reduces average domestic load by 1250 MW, saving 10.7% in energy consumption and lowering unit costs by 12.8% by 2030.
Conclusion:
This study underscores the necessity of indigenous R&D for DSM and renewable energy options to combat climate impacts. Policymakers are encouraged to adopt dedicated frameworks, improve tax incentives, and promote local EED manufacturing. Future work will expand to assess climate impacts on industrial and agricultural sectors and provide detailed socio-economic analyses to strengthen climate resilience strategies.